Among all fungal diseases, mycoses (fungal lesions) of the skin of the feet are the most common. They are also called ringworm or ringworm. Approximately 30% of the population has problems with fungal diseases. Almost half of the patients never take them to the doctor, spreading the fungus among relatives. Microscopic pathogens affect the dermis (skin) or nails. In the latter case, they talk about onychomycosis.
Why are the feet most commonly affected?
There are always various fungi on the skin. Their reproduction is limited by beneficial bacteria and skin secretions. In case of disorders in the work of immunity, changes in the composition of the skin microflora, there is a favorable time for fungi - they can reproduce freely. Infection gateways can serve as regular damage:
- scratches;
- cracks;
- rubbing.
Another cause of mycoses is endocrine disorders. In case of malfunctions in the work of the endocrine glands, not only the balance of hormones changes, but also the work of the entire organism. Including, the composition of skin secretions changes, due to which they lose their bactericidal properties. Fungi can feed on them, which also promotes reproduction.
Other factors also contribute to the weakening of defense forces:
- digestive exhaustion (malnutrition);
- avitaminosis;
- excessive physical and psycho-emotional stress;
- brain concussions;
- regular stress.
These are all non-specific causes of fungal skin lesions. Because of them, mycosis of the feet, the smooth skin of the body or the mucous membranes can develop.
In addition, there are special types of fungi (genus Trichophyton or Microsporum) - pathogenic (pathogenic). In contact with the skin or on its surface, they cause disease. In the case of the feet, the disease is called rubromycosis. On the body, these pathogens form specific spots - lichen. You can get infected from a person or an animal.
The skin of the feet is a special place for fungi. There are always many keratinized cells. Microbes are used as housing and food. "Waking" fungi contribute to sweating of the feet. In closed shoes, a moist environment rich in nutrients is formed on the feet - the "dream" of every fungus. If a person neglects foot hygiene, does not dry and disinfect the shoes, the infection first multiplies in him, and then passes to the feet ofPoor hygiene products, dryness, synthetic socks also contribute to the spread of fungal infection.
Signs of fungus, noticeable visually
Treatment of dermatomycosis is easier the earlier the disease is diagnosed. In advanced cases, the therapy is long-term, includes taking pills and using external means. In the initial stages of mycosis, ointments can be abandoned. It is important to be able to recognize the early symptoms of the fungus in order to go to the doctor in time.
How the fungus looks depends on the form of mycosis. Fungal infection of the feet can appear in 3 different variants, as well as in a mixed form - when there are signs of three main varieties on the feet at the same time.
Intertriginous form
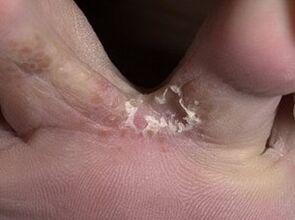
A type of tinea pedis that mainly affects the skin between the toes. The first symptom of the disease is the appearance of a painful crack between the 3rd and 4th or 4th and 5th ring of the foot. The damage is small, but causes inconvenience when washing the feet and walking.
If you look carefully at the wound, a whitish fringe can be seen around it (example in the photo). This is what the edges of the skin around the peeling crack look like. The wound may itch, ooze, enlarge, or vice versa - periodically heal, then reappear.
In some cases, the crack heals, but the skin continues to separate, hyperkeratosis (thickening of the dermis) develops, calluses and calluses appear. In an advanced intertriginous form, the cracks increase (example in the photo), appear between other fingers, the skin is constantly wet. It is difficult for the patient to move, wear any shoes.
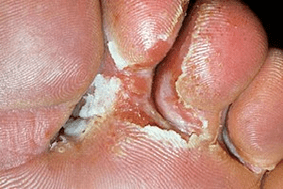
As this form progresses, the crack increases in size. Similar signs appear on the second leg. Thick and large layers of skin are exfoliated around the wound. The second (attached) end is not rejected, and attempts to remove the keratinized part with the fingers end in further damage to the leg.
This type of foot fungus is the most common. The manifestation of pathology in the beginning is not accompanied by any symptoms. As a rule, the infection develops between the 3rd and 4th toe and does not change the color and texture of the skin until a certain point. Then wet cracks and layers of skin appear.
The foot itself remains unharmed, but if the fungus is affected, the feet may sweat more than usual. Fungal therapy of the intertriginous form is characterized by medium complexity.
Dyshidrotic form
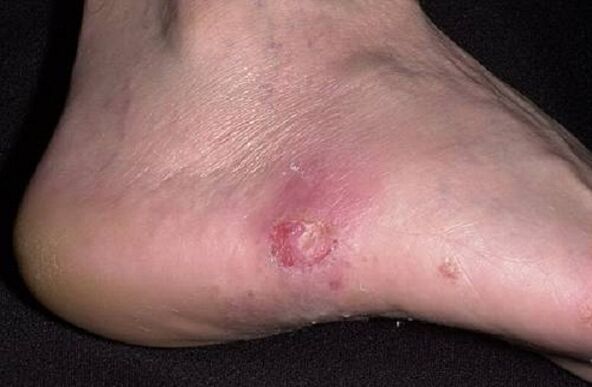
In this form, the first signs of fungus on the skin are blisters on the arch of the foot. Most often - near the heel. The surface becomes dry, deep seals appear on it (feeling like knots). Later, they noticeably rise above the plane of the skin, as they are filled with fluid. Vesicles (vesicles) are usually small - from 2 to 5 mm in diameter. They can merge, forming larger - bullae. Other symptoms include pain and itching around the rash.
The development of the dyshidrotic form of mycosis is manifested by the bursting of blisters. Small or large erosions form in their place. Often they become infected with bacteria and begin to boil. Erosions do not heal for a long time, which makes walking painful. In some cases, erosion disappears and dryness appears in their place.
squamous cell form
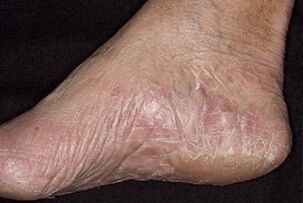
As the disease progresses, severe hyperkeratosis of the feet develops. The size and number of cracks increases. The biggest ones can bleed. Such damages are the way for other pathogenic microbes to enter the body. Because of this, the wounds periodically become inflamed, may abscess. The most common form of foot fungus is manifested by increased dryness of the skin on the plantar part of the limb. This may mean a recent accession of the fungus or, conversely, the result of the development of other forms.
On the arch of the foot and in the center, the dermis becomes dry, thin, shiny, covered with a network of furrows. In the area of the fingers and heels, hyperkeratosis is observed - rapid keratinization, in which the dead particles do not have time to exfoliate. Calluses or calluses form on the front of the foot. There are small cracks on the heels. The entire surface is rough due to pronounced peeling. The patient may feel itching. With prolonged development of mycosis, this symptom is absent.
You can identify foot fungus by excessive dryness, unpleasant odor, itching and constant peeling of the skin.
Onychomycosis
Onychomycosis is a type of foot (or palm) fungus that affects the appendages of the skin - the nails. Nail fungus can be caused by the same pathogens that cause skin mycosis. Get infected with mold and other types of monofungi in the manicure room, on the beach, when you try on new shoes on bare feet, when you go to the sauna or pool. An ingrown toenail can be a contributing factor. The thumb is most commonly affected.
When it hits the nail plate, the fungus begins to divide. It penetrates deep into the nail, spreads over its entire area. The first signs by which you can determine nail fungus are the loss of shine, the appearance of spots (white, yellow, brown, greenish), a change in the shape of the nail plate.
As the disease progresses, the structure of the nail changes in the area of discoloration (it thickens, becomes uneven, loose).
Running toenail fungus looks like thick yellow growths. It is difficult to care for the affected nail plates. Before each haircut, you should take hot baths for your feet. After contact with water, nails become softer and easier to remove with manicure tools.
If the nail fungus is not treated, onycholysis begins - the plate completely or partially exfoliates. After removing the remnants of it, the nail does not always grow back. Sometimes the shedding process ends with a complete loss of nails.
General principles of treatment
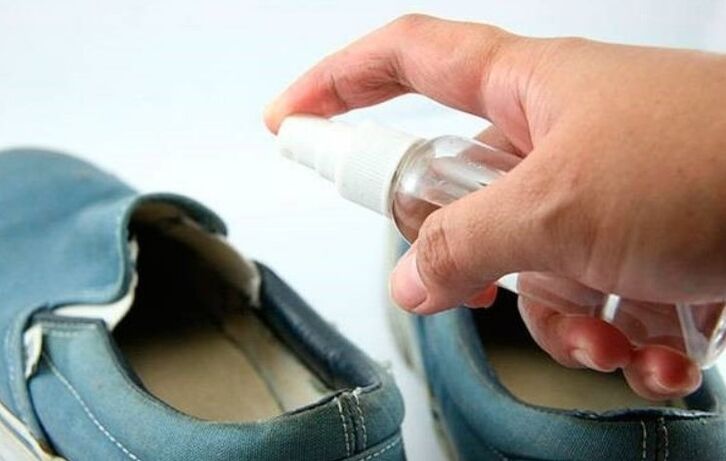

Fungi on the feet are treated with ointments, creams, solutions, special varnishes. In parallel, the patient is prescribed antifungal tablets.
For the entire period of treatment, careful hygiene of the feet, weekly cutting and cutting of the damaged part is indicated. Every day, the patient should remove the keratinized layer of cells from the surface of the feet using a pedicure file.
It is also important to take good care of the shoes - treat them with antifungal drugs or disinfectants. Shoes are dried and aired daily outdoors.
External means
In the initial stage of foot fungus, only ointment or cream is prescribed. Cream and other medicines are prescribed for treatment. They are applied to the skin 1-2 times a day, after thoroughly washing the feet with ordinary soap. Before using creams, it is important that the feet are completely dry. Do not apply the medicine to wet skin. After the treatment, the patient should wear cotton socks.
Tablets
Self-treatment of fungus with pills is impossible. All drugs adversely affect the functioning of the liver and kidneys, have a number of contraindications. Before prescribing a course of antifungal tablets, the specialist will recommend a general and biochemical blood test, which can be used to assess the condition of vital organs.
Nail preparations
Useful in the treatment of onychomycosis and foot fungus. In the first case, they are used to remove the affected part of the nail, in the second - to prevent infection of the nail plates with fungus.
It is most convenient to treat with varnishes - they are applied to the nails 1-2 times a week. The most available drugs for nail fungus are solutions, they are applied to the nails 2 times a day until complete recovery. Special gels are popular. They visually improve the condition of the affected nails, stopping the reproduction of the fungus along the way. Ointments are also prescribed for onychomycosis. They are applied in a thick layer on the affected plates, covered with a bandage and kept like this until the product is completely absorbed. The treatment is repeated twice a day.
Preventing foot fungus is much easier than treating it. To do this, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle, wear your own slippers in the pool and sauna, wash and air your shoes regularly, wear socks made of natural fabric and use anti-perspirant products. In case of regular visits to "wet" establishments, you should use prophylactic antifungal creams - treat the skin of the feet 1-2 times a week.